Try to build a business where every customer only buys from you once…
I dare you.
It can’t be done.
Why?
Because good business — from service-based freelancers to large e-commerce stores — depends on having repeat customers.
Cross selling is one way to get customers to buy from you over and over again, increasing the value you provide, the money they spend, and the longevity of their relationship with your business.
But…
What is it? How do you do it? And what does it look like out in the wild?
In this guide, we’re going to explain cross selling, provide 7 amazing examples, and share 9 mission-critical tips.
Let’s dive in!
Build Your Sales Funnel Now, For Free
What is Cross Selling?
Cross selling is the practice of selling related or complementary products to a customer who has already bought something from you.
This can be done either at the time of purchase or after the customer has received and begun using your product.
The value of cross selling can be summed up by a couple of popularized sales statistics…
- Returning loyal customers spend an average of 33% more per order as compared to others
- 91% of customers are more likely to purchase from brands that provide them with meaningful and relevant offers.
In other words, return customers are very valuable.
And cross selling is one of the best ways to keep your existing customers buying.
But you’ve probably heard a few other terms similar to cross selling, such as “upselling” and “downselling”.
What’s the difference?
The Difference Between Cross selling, Upselling, & Downselling
Cross selling, upselling, and downselling are all terms used to describe ways that you can increase the value and order volume of customer purchases.
However, they each have different definitions and purposes…
Cross selling: Cross selling is when you offer related products to a customer who has already bought something from you. The goal is to sell more products to the customer without detracting from the value of the original purchase.

Upselling: Upselling is when you offer a more expensive version of the product that a customer has already expressed interest in. The goal is to increase the order value by selling a more expensive product.

Downselling: downselling is when you offer a less expensive version of the product that a customer has already expressed interest in. The goal is to capture a sale that might have been lost otherwise.

Ideally, you’ll use all three of these tactics in your sales funnel.
In this guide, we’re going to talk about cross selling specifically. But if you want to learn about upselling or downselling, click the appropriate link.
7 Best Cross Selling Examples We’ve Seen
Cross selling can be done in a number of ways, but it all comes down to offering complementary products to customers who have already bought something from you.
Here are seven of the best examples we’ve seen — each with a slightly different approach.
Example 1. Supplementary Products
Ever go on a shopping spree on Amazon?
It’s probably because of how effective their site cross-sells people who are in buying mode.
One example of this is Amazon’s “Frequently Bought Together” section. They even allow you to add the full package to your basket with a single click and provide the total price.

These products are supplementary to the thing that the customer is already buying. If you bought the camera, you very well might want to also buy a memory card and a case for that specific camera.
So you can see how this works to increase average order value.
Another example of supplementary product cross selling comes from MeUndies, where they offer products to “Complete The Look” based on the product you just purchased.
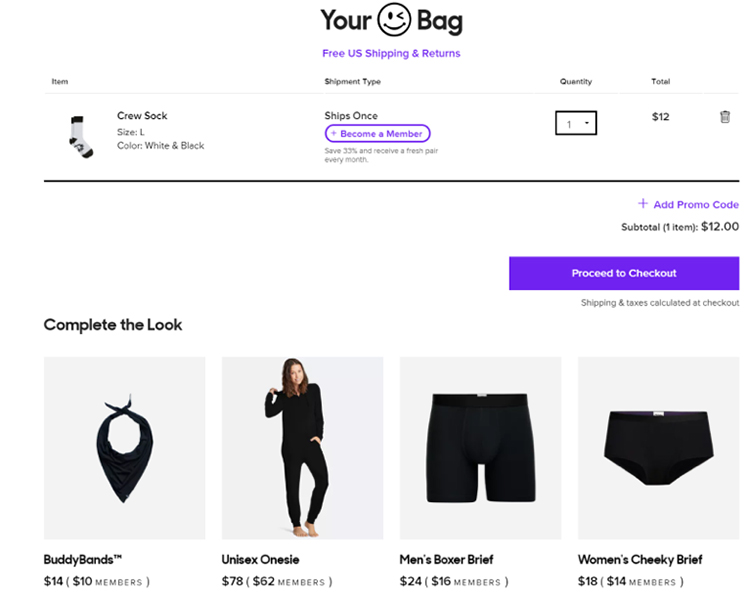
If someone buys part of a set, it’s a good idea to try and sell them the other pieces of that set.
Example 2. Related Products
When we say “related products”, we’re talking about things that aren’t directly supplementary to the item that the customer purchased, but that they might still be interested in.
They’re relevant, but they’re not supplementary.
Here’s an example from UNIQLO, where their “You May Also Like” section offers products that are similar to the style of a product that the customer already expressed interest in.
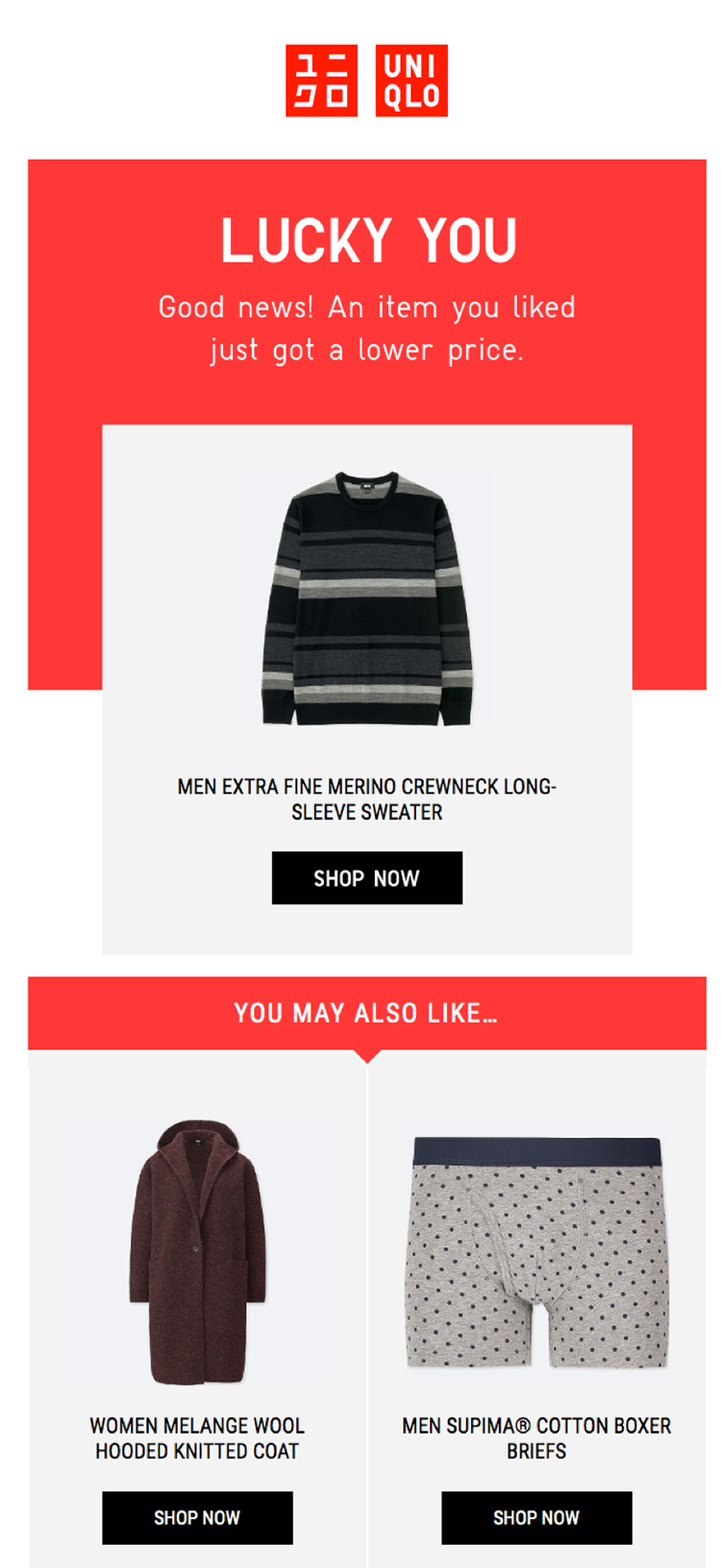
And here’s one more example from a La Mer email recommending similar products to the one that was already purchased.
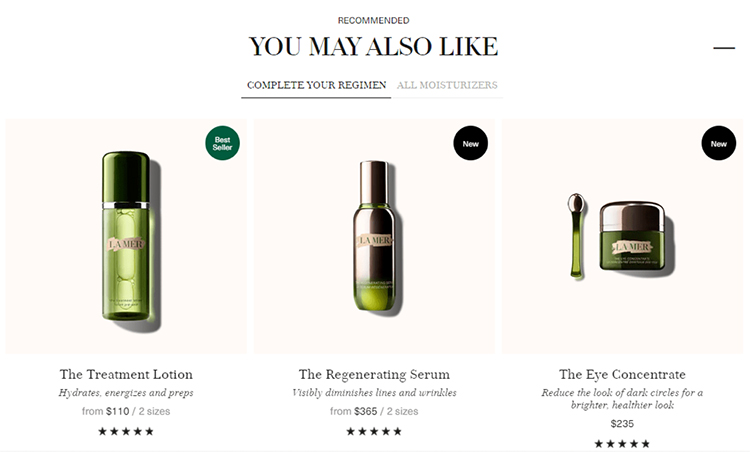
Example 3. Frequent Buyer Behavior
Good behavioral data will allow you to cross-sell with greater results.
If, for instance, you have the ability to track which products in your store people often buy together, then you can reverse engineer your cross selling suggestions to match the behaviors of your existing customers.
After all, if your customers are often buying certain products together, it’s likely that new customers will want to do the same.
Here’s an example of this from Staples, where their “Customers Also Bought These Products” section recommends products based on previous customer behavior.
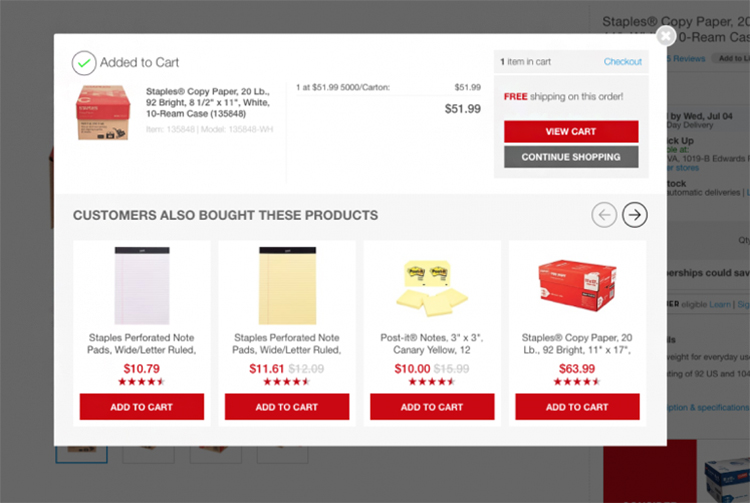
Example 4. Reward Program
It might not technically be counted as cross selling, but having a reward program is a great way to keep your customers coming back for more.
In fact, 68% of customers said they see value in shopping with a brand when the loyalty program sends them personalized discounts based on their purchase history.
Starbucks is great at this.
(Which is why the line is always long)
Their rewards program makes people want to spend more money with them (rather than competitors) by providing points for purchases, which customers can turn into free food and drink.

Sephora does something similar with their rewards program…

Giving your customers rewards is a great way to keep them coming back for more — the more money they spend, the more rewards they get… which makes them want to spend more money.
Win-win-win.
Example 5. Best Sellers
Not sure which products to promote to your new customers?
Don’t have the ability to do some behavioral suggesting wizardry?
Then just recommend your best sellers!
They’re your best sellers for a reason, after all, and recommending them to your new customers is a great way to pull them deeper into your ecosystem.
Here’s an example from L.A. Girl where they recommend “Now Trending” products.
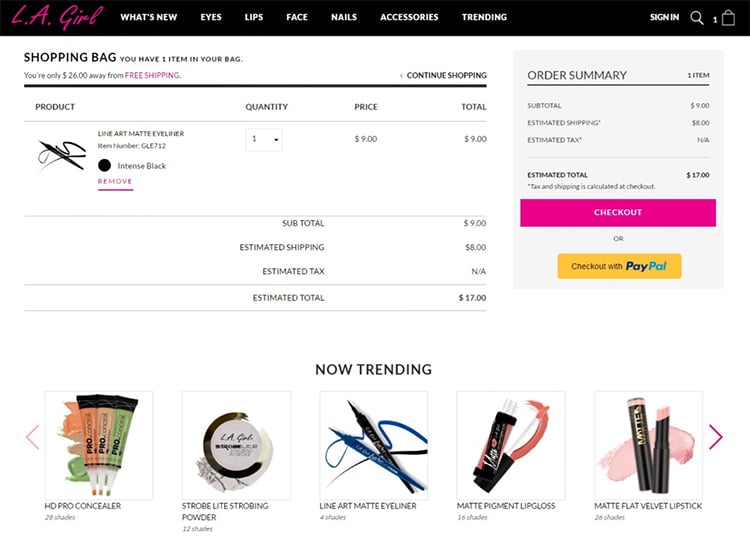
Example 6. Add-Ons
Add-ons are similar to order bumps and allow people to add more products to their existing orders.
Rather than cross selling products to the customer a few days or weeks after their initial purchase, add-ons are available immediately during the checkout process.
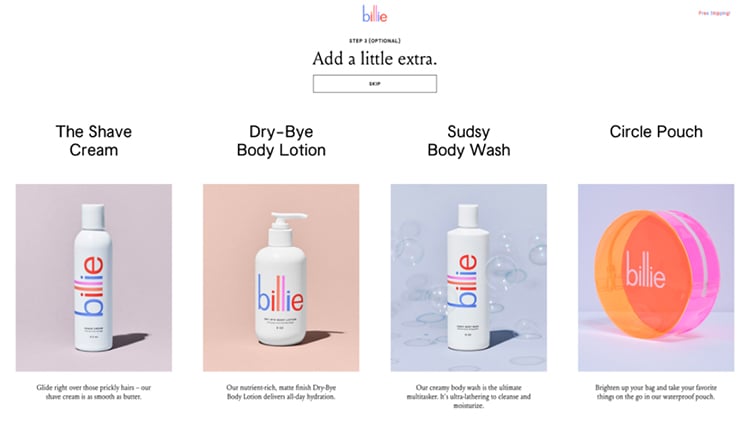
Here’s an example from Billie under the guise of “Add a little extra.”
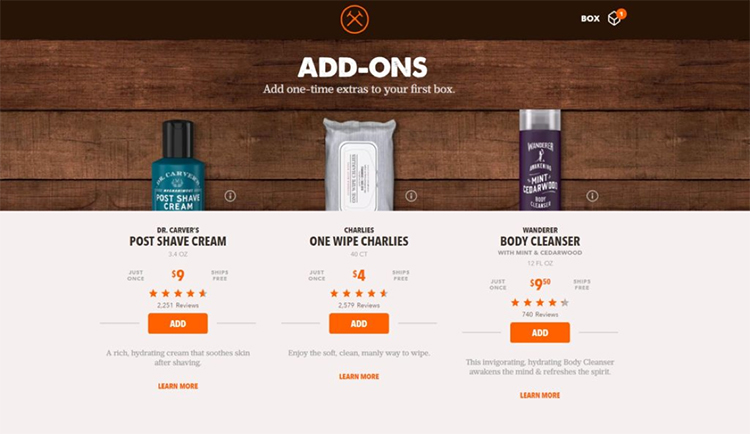
And here’s another example from Dollar Shave Club where they promote add-ons before the customer’s first box ships.
Example 7. Package Discounts
Ever go to Costco and end up buying three TVs instead of one because they had a bulk discount?
No?
Just me?
Well, we’ve all fallen victim to a buy-in-bulk discount at one time or another. Whether it was a giant jar of peanut-butter-filled pretzels, a bag of popcorn, or a small village worth of toilet paper.
That’s because it’s compelling.
Get more, pay less per product (even though you’re paying more in total) — why not!
And that’s a great way to upsell your customers depending on the type of products you offer.
Here’s an example…
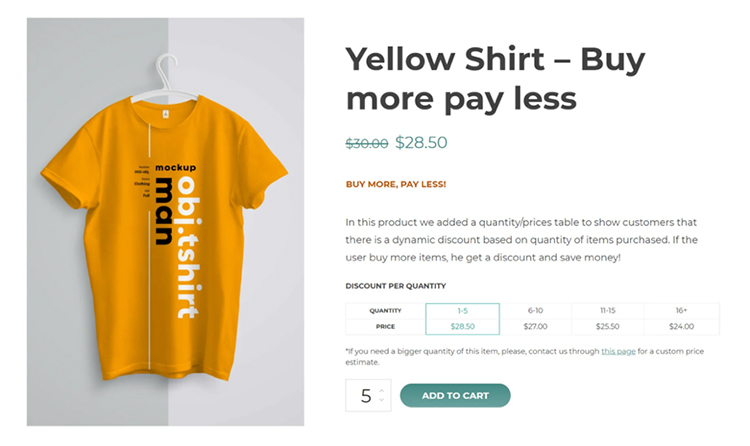
9 Important Cross Selling Tips to Keep in Mind
While there isn’t a one-size-fits-all cross selling strategy, here are some general tips that will help you do it effectively.
1. Use Seinfeld Emails
How often should you cross-sell to your customers?
As often as possible.
In fact, we recommend sending emails with product recommendations every day — the more you email, the more sales you’ll make.
We call these emails “Seinfeld emails”.
Check out the video below to learn how they work.
You might be worried that you’ll annoy your customers by sending emails every day.
But we’ve found that 90% of people don’t care. They’ll just ignore or delete emails that they’re not interested in and they’ll read emails that catch their attention.
Most importantly, you’ll stay top-of-mind and they’ll have an opportunity to buy from you every single day.
Timing is key.
But it’s nearly impossible to predict the right timing for each of your customers — that’s why we recommend emailing daily.
2. Create Automations
The most effective cross selling campaigns are automated.
Why?
Because they allow you to sell the right products to the right customers at the right time without any manual effort.
You can set up an automation in your eCommerce store that sends a follow-up email after someone purchases a product, offering them complementary products or upgrades.
You can also create automatic cross-sells on your product pages, like “Frequently Bought Together” or “Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought”.
3. Consider Timing
it’s important to think about the timing of your cross selling campaign.
For example, if someone just bought a winter coat, they’re probably not interested in buying a bathing suit.
But if you wait a few months and then offer them a discount on a bathing suit when summer hits, they might be more likely to take you up on the offer.
The key is to think about what products complement each other and then offer them at the right time.
4. Follow Your Data
In order to be uber-successful at cross selling, you need to have a good understanding of your customer data.
This includes things like their purchase history, what products customers are interested in, and even their demographic information.
The better you understand your customers, the easier it will be to sell them complementary and relevant products.
5. Limit Number of Recommendations
When you’re making recommendations, it’s important to limit the number of options that you give to customers.
If you give them too many choices, they’ll get overwhelmed and won’t purchase anything.
A good rule of thumb is to limit your recommendations to 3-5 items.
Less is more.
6. Use Limited-Time Offers
When you’re cross selling, creating a sense of urgency can be a great way to increase conversion rate (done in moderation, of course).
For example, you might offer a discount on a complimentary product if it’s purchased within 48 hours of the original purchase.
This gives people an incentive to act quickly.
7. Leverage Social Proof
When you’re making recommendations, make sure to use social proof.
For example, if you’re cross selling a pair of jeans on your product page, you might say something like “Over 90% of customers who bought this item also purchased XYZ”.
This type of social proof helps increase the perceived value of your recommendations and makes people more likely to buy.
8. Make it Easy
When you’re cross selling, make sure it’s easy for people to purchase the product.
If they have to search around your site for 10 minutes to find the product you’re recommending (rather than just “clicking here”), they’re much less likely to buy it.
So make sure the “buy” button is always easy to find.
9. Keep Testing
Finally, it’s important to test different cross selling tactics to see what works best for your store.
There’s no magic formula for success. The only way to know what works is to experiment and see what generates the most sales.
So keep testing different products, different offers, and even different methods for cross selling.
Final Thoughts on Cross Selling
Cross selling is a great way to increase the value of customer orders and boost your average order size.
By following the tips and examples in this guide, you can start implementing effective cross selling tactics in your business today.
Click below if you’re ready to build a killer sales funnel!

